Chile
The data in this note reflect different sub-national geographic levels in OECD countries:
Regions are classified on two territorial levels reflecting the administrative organisation of countries: large regions (TL2) and small regions (TL3). Small regions are classified according to their access to metropolitan areas (Fadic et al. 2019).
Functional urban areas consist of cities – defined as densely populated local units with at least 50 000 inhabitants – and adjacent local units connected to the city (commuting zones) in terms of commuting flows (Dijkstra, Poelman, and Veneri 2019). Metropolitan areas refer to functional urban areas above 250 000 inhabitants.
In addition, some indicators use the degree of urbanisation classification (OECD et al. 2021), which defines three types of areas:
- Cities consist of contiguous grid cells that have a density of at least 1 500 inhabitants per km2 or are at least 50% built up, with a population of at least 50 000.
- Towns and semi-dense areas consist of contiguous grid cells with a density of at least 300 inhabitants per km2 and are at least 3% built up, with a total population of at least 5 000.
- Rural areas are cells that do not belong to a city or a town and semi-dense area. Most of these have a density below 300 inhabitants per km2.
Disclaimer: https://oecdcode.org/disclaimers/territories.html
Regional economic trends
Employment and unemployment rates in regions
In Chile, regional disparities in unemployment rates are moderate compared to other OECD countries. While in Coquimbo and Ñuble 9.2% of the working force was unemployed in 2022Q2, the share was 4.5% in Magallanes and Chilean Antarctica.
Meanwhile, the difference in employment rate between the regions with the highest (Aysén) and lowest (Los Lagos) employment rates reached 20 percentage points in 2022. This places Chile among the top 5 OECD countries in terms of regional disparities in employment.
Note: Harmonised employment and unemployment rates, aged 15 and over. The OECD median corresponds to the median employment rate in large regions.
Source: OECD (2022), “Short-term regional statistics”, OECD Regional Statistics (database)
The first year of COVID-19 on GDP per capita
The first year of COVID-19 resulted in a decrease in GDP per capita in most Chilean regions. Aysén, a region with a GDP per capita 12% above the national average (23 664 vs. 21 176 USD PPP), experienced the largest decrease in GDP among Chilean regions, of approximately -21%.
Note: GDP per capita is measured in constant prices and constant PPPs, reference year 2015. Constant prices are calculated using national deflators. The OECD median corresponds to the median decline in GDP per capita observed across OECD large regions over the period.
Source: OECD (2022), “Regional economy”, OECD Regional Statistics (database)
Trends in regional economic disparities in the last decade
Differences between Chilean regions in terms of GDP per capita have decreased over the past nine years. Growth in the lagging and decline in the richer regions has driven such decrease.
Note: The GDP per capita of the top and bottom 20% regions are defined as those with the highest/lowest GDP per capita until the equivalent of 20% of the national population is reached. A ratio of 2 means the richest regions have a GDP per capita twice as large as the poorest regions. The indicator is calculated using large regions, except for Latvia and Estonia, where small regions are used instead. Irish GDP underwent an upwards revision in 2016. Care is advised in its interpretation.
Source: OECD (2022), “Regional economy”, OECD Regional Statistics (database)
Productivity trends in the last decade
Between 2013 and 2019, Los Lagos and Antofagasta experienced the highest and lowest productivity growth in Chile, respectively. Los Lagos saw a labour productivity increase of 5.1% per year, above the OECD average of 0.9%1. During the same period, Antofagasta experienced a decline in measured labour productivity, averaging -2.9% per year.
Less than half of Chilean regions experienced a decline in labour productivity between 2019 and 2020. Antofagasta experienced the largest decline, with a drop of 28.3%
Note: Regional Gross Value Added (GVA) per worker, in USD, constant prices, constant PPP, base year 2015.
Source: OECD (2022), “Regional economy”, OECD Regional Statistics (database)
Well-being, liveability and inclusion in regions
Regional well-being
Chile faces stark regional disparities across eight well-being dimensions, with the starkest disparities in terms of community, environment and life satisfaction.
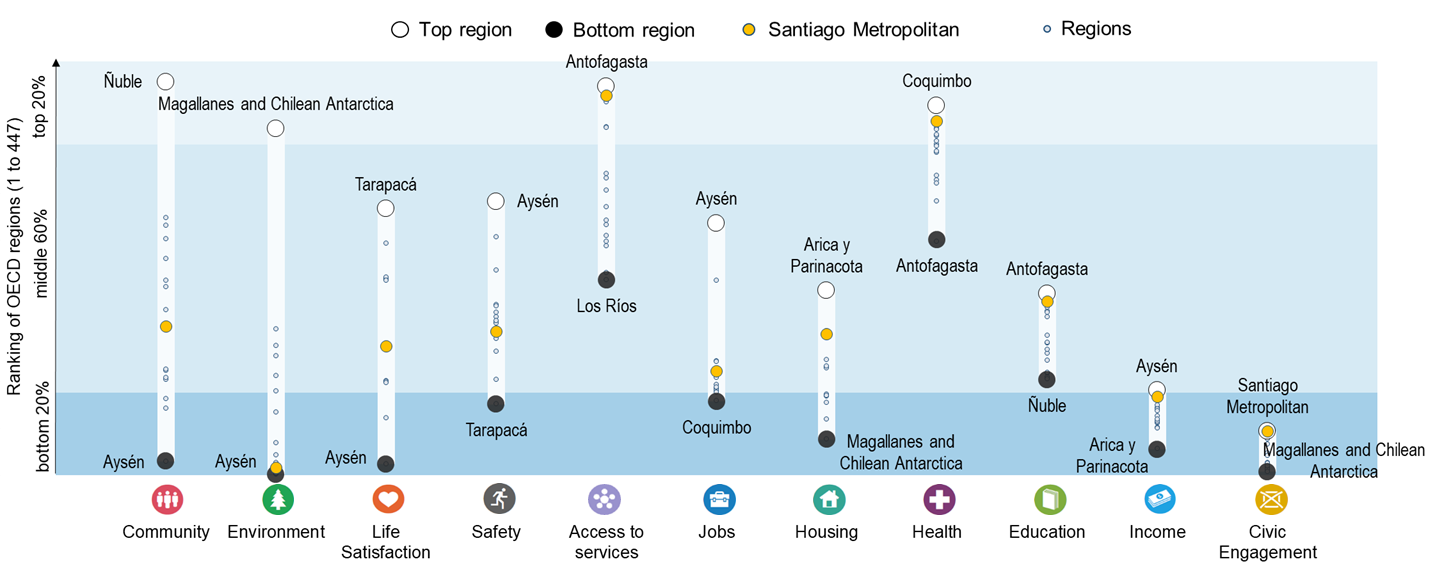
Note: Regional indices provide a first comparative glance of well-being in OECD regions. The figure shows the relative ranking of the regions with the best and worst outcomes in the eleven well-being dimensions, relative to all OECD regions. The eleven dimensions are ordered by decreasing regional disparities in the country. Each well-being dimension is measured by the indicators in the table below.
Relative to other OECD regions, Chile performs best in the health dimension, with 50% of of Chilean regions lying in the top 20% of OECD regions.
The top 20% of Chilean regions rank above the OECD median region in 4 out of 14 well-being indicators, performing best in terms of life expectancy at birth and perceived social network support.
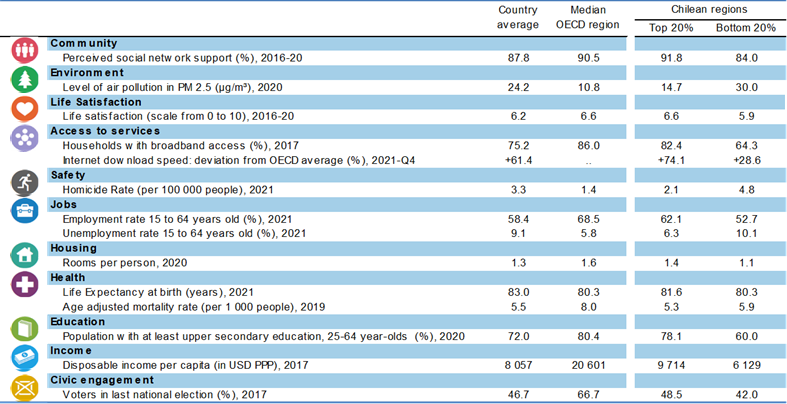
Note: Regional well-being indices are affected by the availability and comparability of regional data across OECD countries. The indicators used to create the indices can therefore vary across OECD publications as new information becomes available. For more visuals, visit https://www.oecdregionalwellbeing.org.
The digital divide
Fixed Internet connections in Chilean cities and rural areas deliver speeds significantly faster than the OECD average (48% and 5%, respectively). This gap (43 percentage points) is larger than in most other OECD countries.
Note: Cities and rural areas are identified according to the degree of urbanisation (OECD et al. 2021). Internet speed measurements are based on speed tests performed by users around the globe via the Ookla Speedtest platform. As such, data may be subject to testing biases (e.g. fast connections being tested more frequently), or to strategic testing by ISPs in specific markets to boost averages. For a more comprehensive picture of Internet quality and connectivity across places, see OECD (2022), “Broadband networks of the future”.
Source: OECD calculations based on Speedtest by Ookla Global Fixed and Mobile Network Performance Maps for 2020Q4.
The average speed of fixed Internet connections is above the OECD average in all Chilean regions. Within the country, residents of Antofagasta, Magallanes and Chilean Antarctica and Santiago Metropolitan Region experience the fastest connections.
Relative poverty rates
In Chile, relative poverty rates2 range from 14% to 39% across regions. This 25 percentage point difference is more pronounced than the average difference observed across the 29 OECD countries with available data (16 percentage points).
Note: The OECD median gives the median relative poverty rate observed in a sample made of 326 large regions (from 28 countries), and 28 small regions (from Denmark, Lithuania and the Slovak Republic). Data corresponds to 2020 or the latest available year.
Demographic trends in regions and cities
Dependency rate
The elderly dependency rate3 in Chile is also lower than the OECD average (26.8 %) in all regions, ranging from 23.5% in Ñuble to 11.4% in Antofagasta.
Population in cities
Between 2010 and 2022, all cities in Chile experienced a rise in population. Population growth ranged from 0.3% per year in Calera to 2.2% per year in Coquimbo-La Serena.
Note: Cities refer to functional urban areas (Dijkstra, Poelman, and Veneri 2019). Population counts for the functional urban area are aggregated from administrative, municipal-level, data.
Over the past decade, the population has grown the most in Chilean cities with more than 1.5 million inhabitants. Cities with 50 000 to 100 000 inhabitants have seen their population grow, on average, but to a lesser extent.
Environmental challenges in regions and cities
Greenhouse gas emissions in regions
Since 1990, production-based greenhouse gas emissions have increased in most Chilean regions. Ñuble (340%) and Magallanes and Chilean Antarctica (-44%) experienced the largest increase and decrease in emissions, respectively.
Note: Bubbles are proportional to per capita greenhouse gas emissions, not to the overall level of greenhouse gas emissions in the region.
Source: OECD calculations, based on the Emissions Database for Global Atmospheric Research (European Commission. Joint Research Centre. 2019).
In 2018, greenhouse gas emissions per capita in Chile were largest in Atacama, Magallanes and Chilean Antarctica and Antofagasta. Power accounts for the largest share of greenhouse gas emissions in Atacama and Antofagasta, while the transport sector accounts for most emissions in Magallanes and Chilean Antarctica.
Note: Regions with low population counts may rank high in greenhouse gas emissions per capita while contributing relatively little to overall emissions in the country.
Urban heat island effect
In Chilean cities, the difference in temperature between cities and their surrounding areas (i.e. urban heat island intensity) reaches 0.3 degrees Celsius (°C). The largest effect is observed in Osorno and Punta Arenas, two cities that are, on average, 2.8°C and 3.9°C warmer than their surrounding areas, respectively.
Note: The Urban Heat Island Intensity (UHI) index is defined as the difference in land surface temperature between built-up areas and non-built-up areas within functional urban areas. This index can be affected by the type of vegetation and climate in non-built-up areas.
Source: OECD calculations, based on land surface temperature data from NASA’s Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) (Wan, Hook, and Hulley 2021a, 2021b)
References
Source of administrative boundaries: © OECD, © EuroGeographics, National Statistical Offices, © UN-FAO Global Administrative Unit Layers (GAUL)
Footnotes
International comparability in 2019 and 2020 is limited because of methodological differences in the calculation of employment counts during the height of the COVID-19 economic crisis.↩︎
The relative poverty rate gives the share of people – as a % of the regional population – with an income below the relative poverty line (60% of the national median income).↩︎
The elderly dependency rate compares the number of elderly people at an age when they are generally economically inactive (i.e. aged 65 and over), to the number of people of working age (i.e. 15-64 years old).↩︎
